Cryptocurrency trading is often seen as a highly volatile and unpredictable market. While no trader can completely eliminate risk, there are well-established techniques that help minimize losses and improve long-term profitability. In this comprehensive we explore A–Z strategies, tools, and proven principles that allow traders to approach the market with confidence and discipline. Below are 10 essential chapters, offering a deep dive into smarter and safer crypto trading.
1. Understanding Market Foundations (A–Z Basics Every Trader Must Know)

Before applying risk-reduction strategies, every trader must understand the foundations of cryptocurrency markets. Crypto operates 24/7 without a central authority, which makes it more volatile than stocks or commodities. This constant volatility is both an opportunity and a threat—prices can rise rapidly, but they can also crash in minutes. To trade with minimal loss, traders must first grasp market structures, liquidity levels, and order types.Liquidity refers to how easily a trader can buy or sell an asset without drastically affecting the price. Coins with low liquidity tend to have erratic price movements and slippage. Understanding this helps traders choose safer assets.
Market psychology also plays an important role. Fear, greed, panic, and hype influence price behavior far more than traditional financial markets. Traders who recognize emotional patterns—such as FOMO or capitulation—have a higher chance of staying disciplined.
Another essential foundational concept is blockchain technology itself. Knowing how networks like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and others function can help traders identify strong long-term projects vs. speculative coins with no utility. Stronger projects tend to be safer during volatility.
Finally, traders must familiarize themselves with basic trading tools, exchanges like Swaptime.io, charting platforms, and market indicators. A solid foundation prevents emotional decision-making and prepares new traders for advanced strategies that reduce losses.
2. Technical Analysis Techniques (Reading Charts to Avoid Bad Trades)
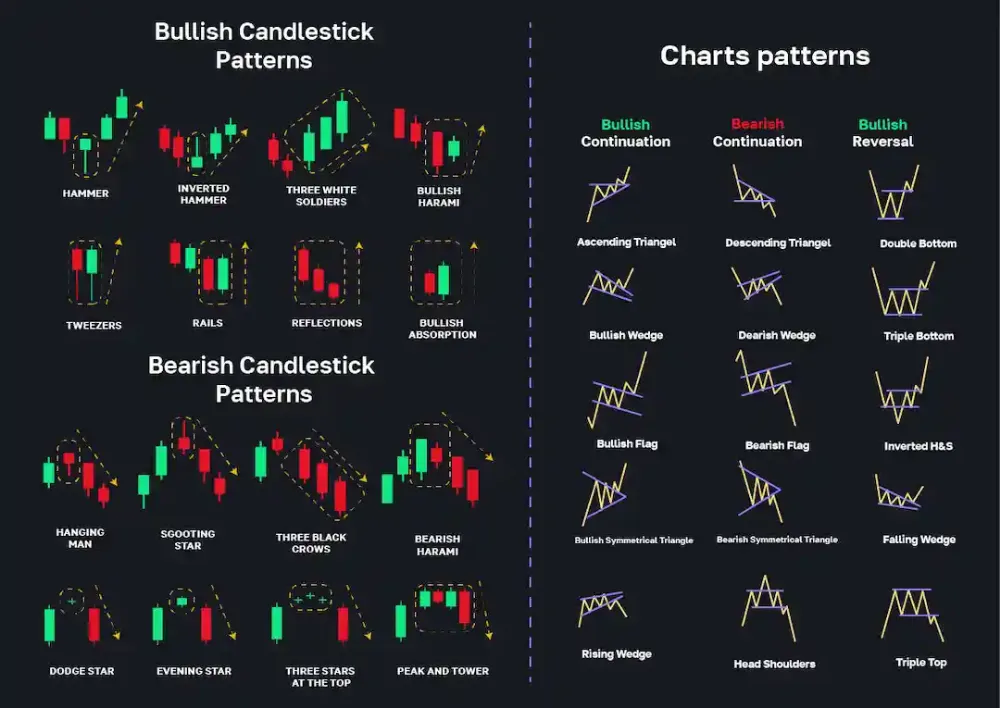
Technical analysis (TA) is one of the most important tools for avoiding unnecessary losses. By learning how to read charts, traders can detect market trends, momentum shifts, and potential entry or exit points. The most common TA tool is the candlestick chart, which displays asset movements over specific periods.
Candlestick patterns—such as doji, hammer, engulfing, and shooting star—help traders predict potential reversals. Recognizing these patterns prevents entering trades during unstable price action.
Trendlines and channels help identify whether the market is bullish, bearish, or moving sideways. Traders who trade with the trend typically face lower risks because they move with the majority of market momentum. When price breaks out of a long-term channel, it often signals the beginning of a new trend.
Indicators are another critical component. Tools like RSI (Relative Strength Index), MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence), and Bollinger Bands help determine overbought and oversold zones. Entering during oversold conditions and exiting during overbought conditions improves the likelihood of profitable trades.
Support and resistance levels are also crucial. These levels show where price historically bounces or gets rejected. Traders use them to set better stop-losses and avoid impulsive buy-ins at peaks.
Mastering technical analysis does not guarantee perfect results, but it significantly increases the probability of avoiding bad entries and emotional trades.
3. Fundamental Analysis (Evaluating Projects Before Buying)

While technical analysis focuses on charts, fundamental analysis (FA) focuses on the underlying value and future potential of a project. This is essential for minimizing losses, especially in long-term investments.
Fundamentals include evaluating a project’s use case, development team, roadmap, tokenomics, and competitor landscape. Traders should analyze whether the project solves a real problem, has active development, and is supported by a strong community.
Tokenomics is one of the most overlooked aspects. Projects with high inflation or unlimited token supply may lose value over time. Conversely, tokens with capped supply or strong burn mechanisms may appreciate in value if demand grows.
Another FA technique is monitoring partnerships, exchange listings, and ecosystem growth. News events often affect price movements, and traders who follow these updates avoid entering trades right before major selling pressure hits.
Whitepapers offer valuable insights into a project’s vision, technology, and scalability. While not every detail needs to be understood, recognizing red flags—such as unrealistic promises or missing technical explanations—helps traders avoid risky investments.
Fundamental analysis does not guarantee profit, but it significantly reduces the chances of buying into worthless or pump-and-dump projects that often lead to heavy losses.
4. Risk Management (The Most Critical Tool for Avoiding Losses)
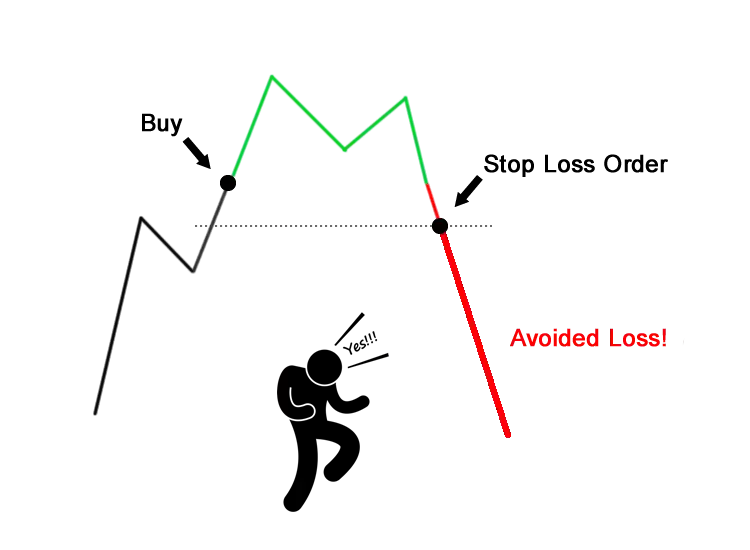
Risk management is the backbone of successful trading. No matter how accurate your technical or fundamental analysis is, poor risk management can wipe out your portfolio in a single bad trade.Position sizing is the first rule. Traders should never put their entire capital into one trade. A common rule is the 1–3% risk rule, meaning only 1–3% of the portfolio is risked per trade. This protects the trader during unexpected market movements.
Setting stop-loss orders is essential. A stop-loss automatically closes a trade when the price falls below a predetermined level. This prevents emotional decision-making and protects from drastic losses during sudden crashes.
Diversification is another important principle. Investing in multiple projects and categories spreads risk and prevents catastrophic losses if one asset collapses. Diversification should include large-cap, mid-cap, and selective high-potential projects.
Another technique is hedging—using stablecoins during uncertain market conditions. Rotating part of the portfolio into USDT or USDC protects traders during extended downtrends.
Finally, traders must avoid over-leveraging. While leverage amplifies gains, it also amplifies losses. Many beginners lose entire portfolios using high leverage, especially in volatile markets like crypto.
Proper risk management ensures survival in the long run, which is the true secret behind successful trading.
5. Psychological Discipline (Controlling Emotions in Volatile Markets)
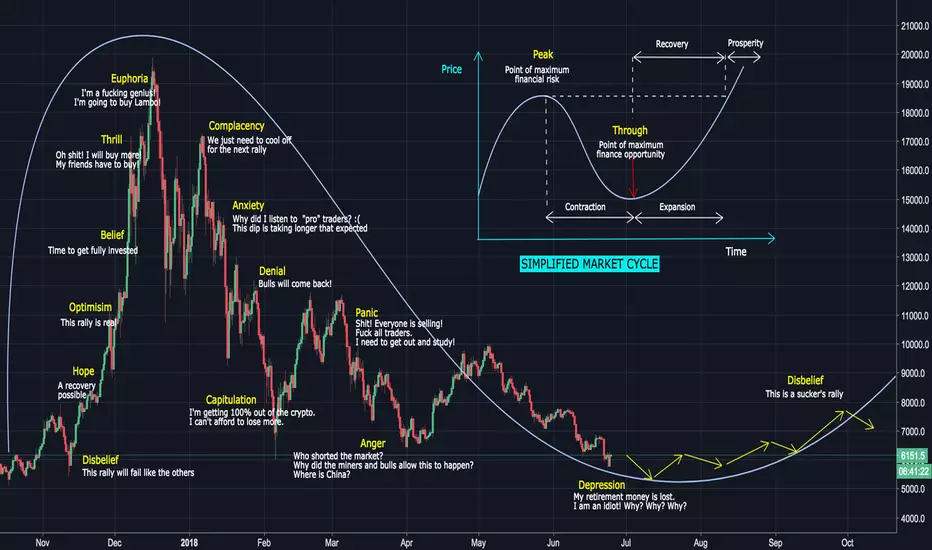
Emotions are one of the biggest enemies of crypto traders. Fear, greed, FOMO (fear of missing out), and FUD (fear, uncertainty, doubt) often lead to irrational decisions. Emotional traders tend to buy tops, sell bottoms, or hold losing positions for too long.Psychological discipline begins with having a trading plan. Traders should determine entry, exit, and stop-loss levels before entering any trade. Following the plan prevents impulsive decisions based on market noise.
Greed is a major factor in losses. Many traders fail to take profit because they hope for higher gains. A structured profit-taking strategy—such as selling 25% at different levels—helps lock in gains while maintaining exposure.
Fear also causes major losses. During corrections, inexperienced traders panic-sell even when the long-term trend remains intact. Recognizing the difference between short-term volatility and long-term reversals gives traders confidence during market dips.
Another psychological tool is avoiding over-trading. Many traders chase every price movement, which increases stress and leads to unnecessary losses. Practicing patience and entering only high-probability setups improves performance.
Finally, traders should avoid trading when exhausted or emotional. Clear thinking is essential for managing risk and making rational decisions.
6. Using Stop-Loss, Take-Profit, and Trailing Stops

Stop-losses, take-profits, and trailing stops are powerful tools that help automate risk management and protect profits. Many traders underestimate these tools, but they are essential for minimizing losses.A stop-loss protects traders by closing the trade if the price moves against them. Traders should place stop-losses below support zones and avoid placing them too tight, which may cause premature liquidation.
A take-profit order automatically closes the trade when the price reaches a profitable level. This prevents traders from overthinking or waiting too long for higher prices. Multiple take-profit levels—such as TP1, TP2, and TP3—help secure profits strategically.
A trailing stop is one of the most advanced tools. It follows the price as it moves upward but locks profits if the trend reverses. This allows traders to ride major trends while minimizing downside risks.
Combining these tools ensures balanced risk protection. They automate decision-making, reduce emotional interference, and help traders follow disciplined strategies.
7. Using Multiple Timeframes (MTF Strategy to Reduce Bad Entries)
Multi-timeframe (MTF) analysis is a strategy that helps traders avoid entering trades during weak or confusing market conditions. Traders often lose money by only looking at short-term charts, such as the 5-minute or 15-minute timeframe.MTF analysis begins with identifying the general market trend on higher timeframes—such as the 1-day or 4-hour chart. If the higher timeframes show a clear uptrend, traders should avoid taking short positions. Trading against the major trend increases risk significantly.
Next, traders zoom into smaller timeframes to find precise entries. Support and resistance levels become clearer on these smaller charts, helping identify optimal entry zones.
MTF analysis also helps spot divergences between indicators on different timeframes, which often signal trend reversals. This reduces the risk of entering trades when the overall momentum is weakening.
8. Portfolio Management (Balancing Assets to Reduce Overall Risk)

Portfolio management involves allocating assets based on risk tolerance, market conditions, and long-term goals. A well-structured portfolio prevents devastating losses.Traders should categorize assets into high-risk, medium-risk, and low-risk groups. Large-cap cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum generally carry lower risk, while smaller altcoins carry higher risks but offer higher potential returns.
Dollar-cost averaging (DCA) is an excellent portfolio strategy. By investing a fixed amount regularly, traders avoid buying tops and reduce emotional decisions.
It’s also important to rebalance the portfolio periodically. When one asset grows too large compared to others, traders should redistribute profits to maintain diversification.
9. Safe Trading Tools & Platforms (Using Reliable Exchanges & Wallets)
Using secure platforms is essential for minimizing risk. Exchanges like Swaptime.io offer user-friendly interfaces, fast swaps, and reliable performance—important features for smooth trading without delays or slippage.Traders must use secure wallets—such as hardware wallets—for long-term storage. Keeping assets on exchanges increases the risk of hacks.
Security also involves enabling two-factor authentication (2FA), avoiding suspicious links, and using trusted networks.
10. Long-Term vs Short-Term Strategies (Choosing the Right Method)
Traders must choose strategies that align with their risk tolerance. Long-term investing (HODLing) is generally safer than day trading because it focuses on strong projects and overlooks short-term volatility.Short-term strategies like scalping and day trading require skill, discipline, strong technical analysis, and consistent execution. These methods offer higher potential returns but also come with higher risk.
Blending long-term and short-term strategies often creates a balanced approach that minimizes loss while maximizing opportunity.
